Excuse me, can you speak English?
He will be escorting you to your cage….
What is the SOP?
PUE of 1.4.
Check out the server on RU30 for Rack 3.14.
Energize the PDU.
Where is Colo?
Is that a Cat 6 or Cat 6A?
If you work in a data center then some of the terms above will be familiar to you. However, as new graduate engineers get their first working opportunity in a Data Center environment, they can be overwhelmed by the number of industry terms and abbreviations being used on them in daily communications. They will surely pick up the terms over time. However, understanding what some of it means is important as it can be detrimental especially for carrying out Remote Hands or other facilities works in a Data Center. A very good simple piece of advice that I have received during my engineering days and I still use it today is, “Never assume and always ask until it’s clear for you.”
In part 5 of the Everything about Remote Hands series, we will share and clarify some of the more common terminologies you should know if you plan to work in a Data Center.
There are numerous terminologies used in the data centers and since our main focus in this series is on Remote Hands, we shall discuss the common terminologies that every Remote Hands Engineer should know. Hope this helps.
TERMINOLOGIES USED IN THE DATA CENTER
SOP – Standard Operating Procedure:
This is one of the most important documents you will need to read and know them by hard for any operational staff working in a Data Center. It’s a document that will need to be reviewed and referred to when in doubt. A Standard Operating Procedure is a step-by-step instruction created by the organization to help the Remote Hands team and staff to carry out routines and regular tasks. SOPs target to achieve efficiency, quality delivery, and uniformity of performance, prevents miscommunication and any possible failure to comply with the industry standards. Without these set guidelines, each person may perform and complete the task in his or her own way. It will also help to complete tasks fast and safest possible way.
SLA – Service Level Agreement:
Service-Level Agreement (SLA) is a commitment between the service provider and the client defining the level of service expectations by a client from the service provider, laying out the metrics by which that service is measured, and the remedies or penalties, if any, should the agreed-on service levels are not being achieved.
RU or U – Rack Unit:
Rack Units (RU) were created by the Electronic Industries Alliance (“EIA”) to help standardize equipment used by telecommunications carriers. RU is a unit of measurement used to describe the dimensions of equipment that have to be placed inside the data center rack. Servers and related components that are to be mounted on the racks are specified in multiple RU like 1U, 2U, 4U, etc. 1RU is equal to 1.75 inches or 44.45mm. The Remote Hands team will use them to identify the actual location of where the equipment should be mounted within the specific rack.
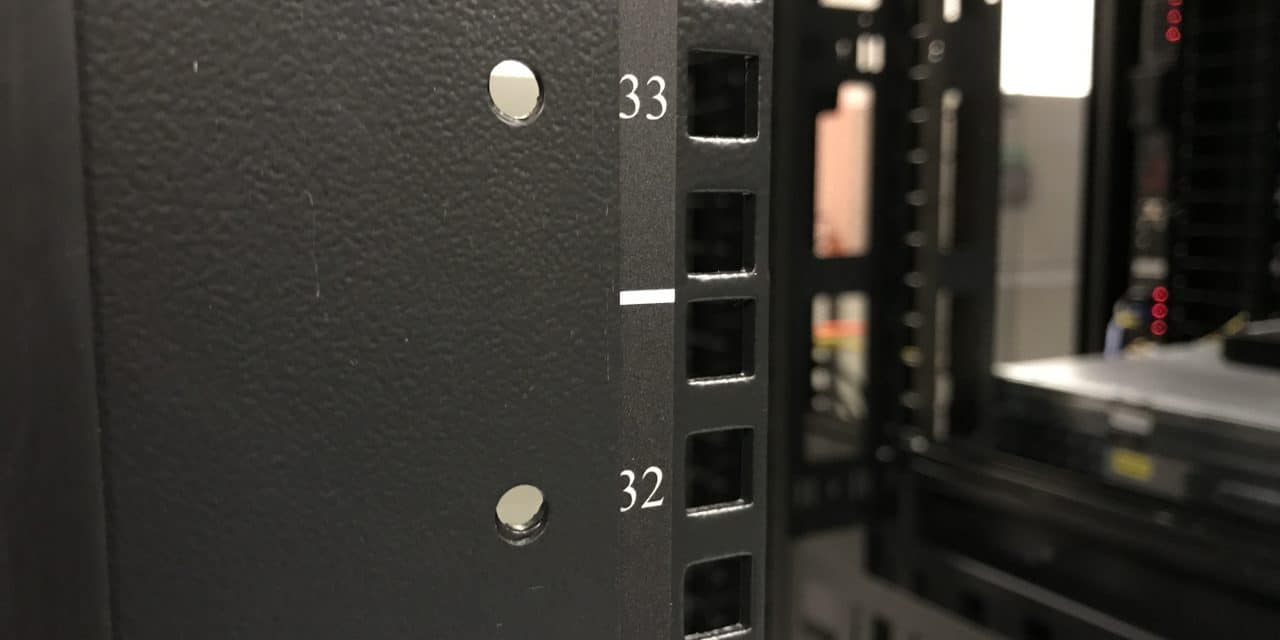

RU33 & RU 32 on a 19″ Server Rack
PDU – Power Distribution Unit:
There are various types of power distribution units (PDU). It can be a cabinet, rack-mounted strips, and even mobile portable ones. PUDs are fitted with multiple outputs designed to distribute electric power, especially to racks for IT components, servers, and networking equipment located within a data center. Racks in data centers are typically provided with dual PDUs connected to 2 separate power sources. The Remote Hands team always ensures that the equipment power sources will never be connected to the same or single PDU.
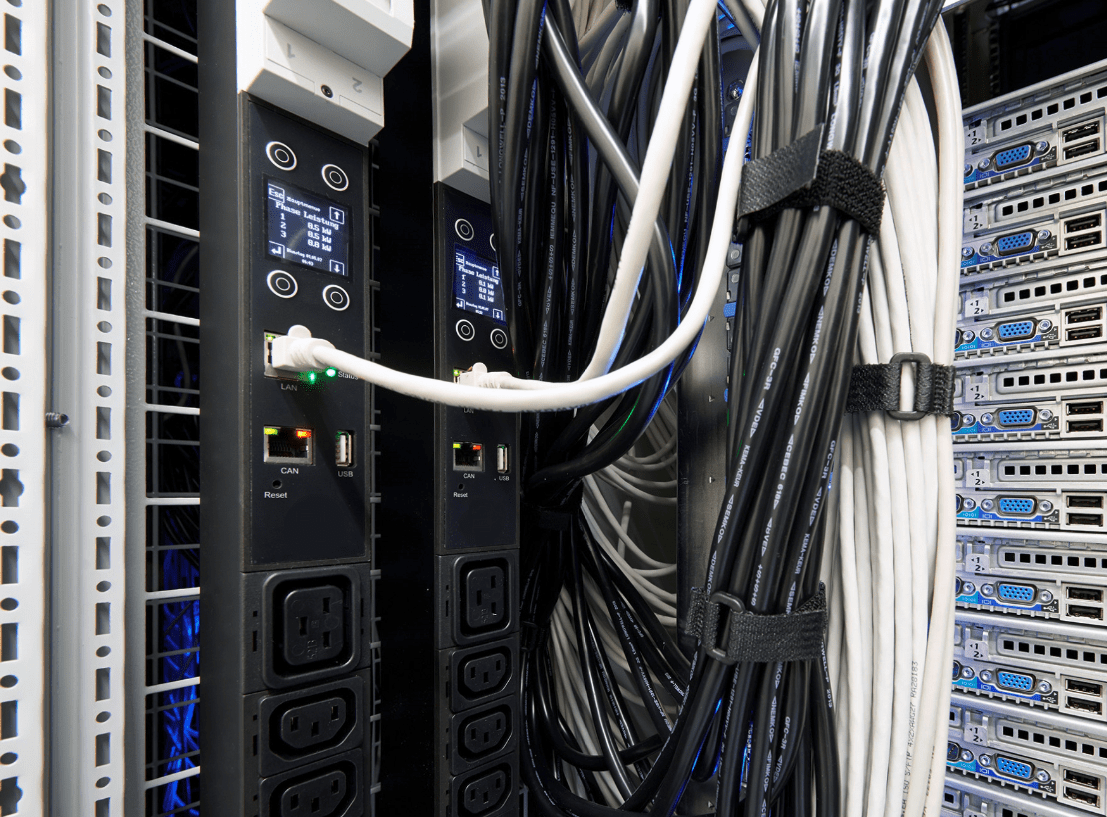
Rack Mounted PDUs
UPS- Uninterruptible Power Supply / Systems / Source:
UPS is electrical equipment that is part of the critical data center component that cleans incoming “dirty” power from the commercial utility power and provides emergency and backup power to equipment when the main power source fails. These back units are provided to avoid any downtime due to power failure and interruptions.
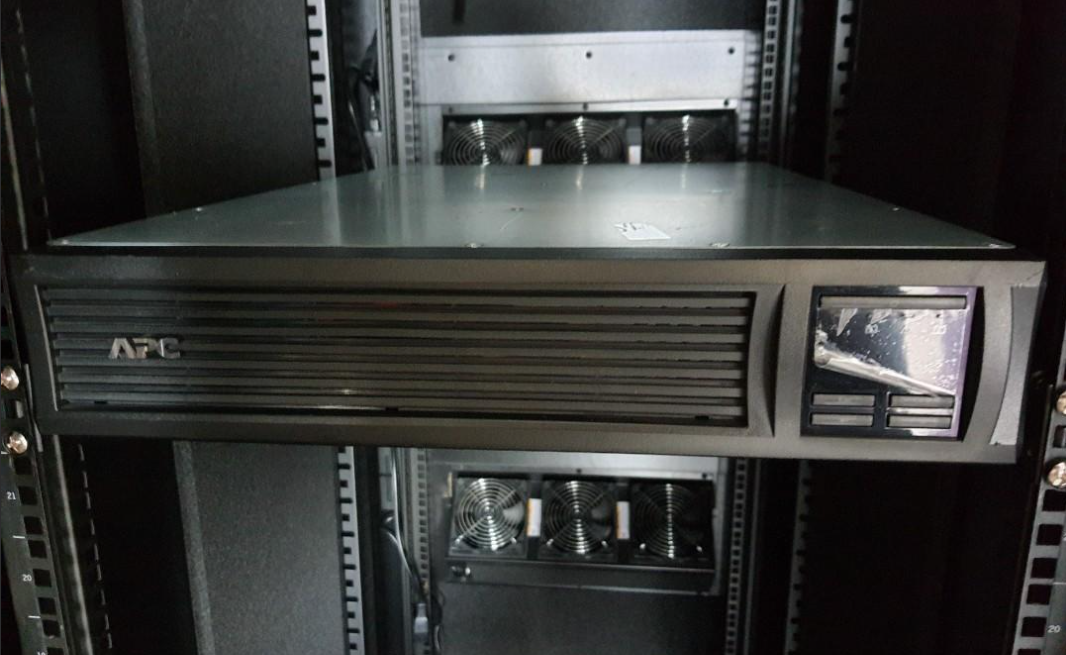

Rack Mount UPS
Cable Baskets or Wire mesh Cable Tray:
Cable Baskets are also sometimes called wire mesh cable trays because of how they are constructed out of wire mesh material and support the data cables going from one point in the data center to another. For example, data cables going from MMR to COLO can be designed with cable baskets.
The Remote Hands team can easily assess the fill rate and space availability due to the open wire mesh structure, which helps to plan the route for new cable installations.
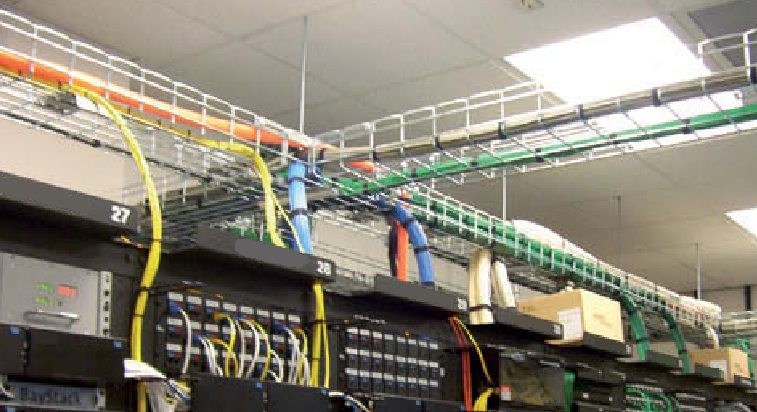

Cable Basket above the open racks
Fiber Runners:
A fiber runner is a pathway/channel designed to carry fibers connecting from one place to another mainly between racks. Fiber runners are used to carrying fiber which is delicate and is used to carry fiber locally. They are very easy to install and the Remote Hands team can lay the fiber cables into the fiber runners in a breeze.
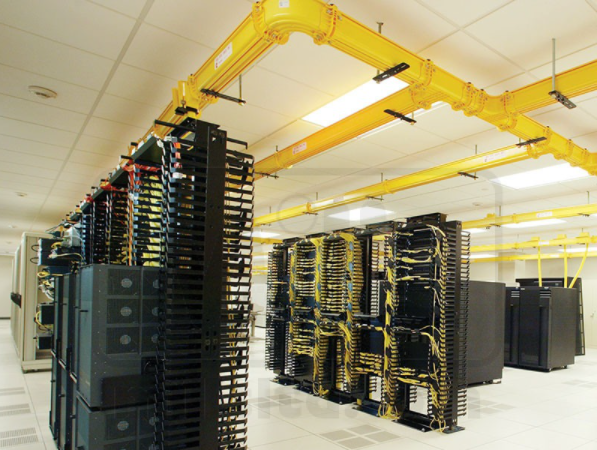

Yellow Fiber Runner installed above racks.
CAT X
CAT is the abbreviation for Category. The X here refers to the different number or standard for a copper structured cable. In data centers, we prefer to use at least a CAT 6A twisted pairs copper cable or above standards are used for the interconnectivity of the systems such as servers and network equipment.

CAT 6A Patching
Cross-Connect:
One of the most common tasks carried out by the Remote Hands team is the cross-connect provisions in the data center. Cross-Connect is the physical cable that provides a direct connection between two different locations within a data center. Cross-connect allows colocation clients to establish dedicated high-performance connections within the data center. This provides greater reliability and lower latency on network connections that are used by default outside of a data center.

Fiber cross-connects are the veins of a data center.
MMR- Meet-Me Room:
MMR is an important physical area within the data center where Internet service providers, telecommunication carriers, cable companies converge together in a secure room to interconnect and cross-connect with each other and the distribution of services to other areas in the data center. This is also where the Remote Hands team spends quite a fair bit of time working in.

MMR housing multiple carriers and cross-connection service.
MDF Room – Main Distribution Frame Room:
MDF Room is a demarcation point in the data center serving as the main termination point for telecommunication providers and carriers, similar to a local telephone and internet exchange. The MDF that is housed in this room is used to interconnect and manage telecommunications cables between themselves and many other intermediate distribution frames throughout the data center.
COLO- Colocation:
Colocation in a data center is referred to as space where bandwidth, space, and equipment are available for rent to retail customers. The Remote Hands team’s most frequent area works in, where rack and stacks, testing, and installation activities are being carried out.
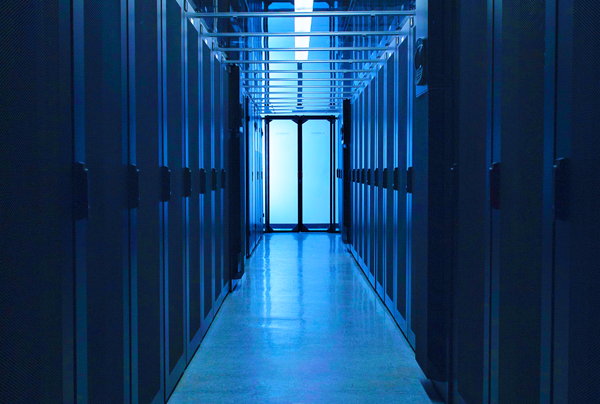

Typical Colocation space in the data center
Cage
A cage is an enclosure built to subdivide a secure space into colocation areas within the data center using mesh walls, sliding doors, security panels, cameras, etc. Similar to the zoo, yes a zoo. Data Center cages provide a secure separation from unauthorized access and some cages have full visibility into what’s inside but from a safe distance.

Typical secure cage colocation
Rack & Stack:
Rack & Stack as the term implies commonly used by the data center Remote Hands team to mount (racking) and install (stacking) the servers and any IT equipment typically through the service request portals by the data center operators.
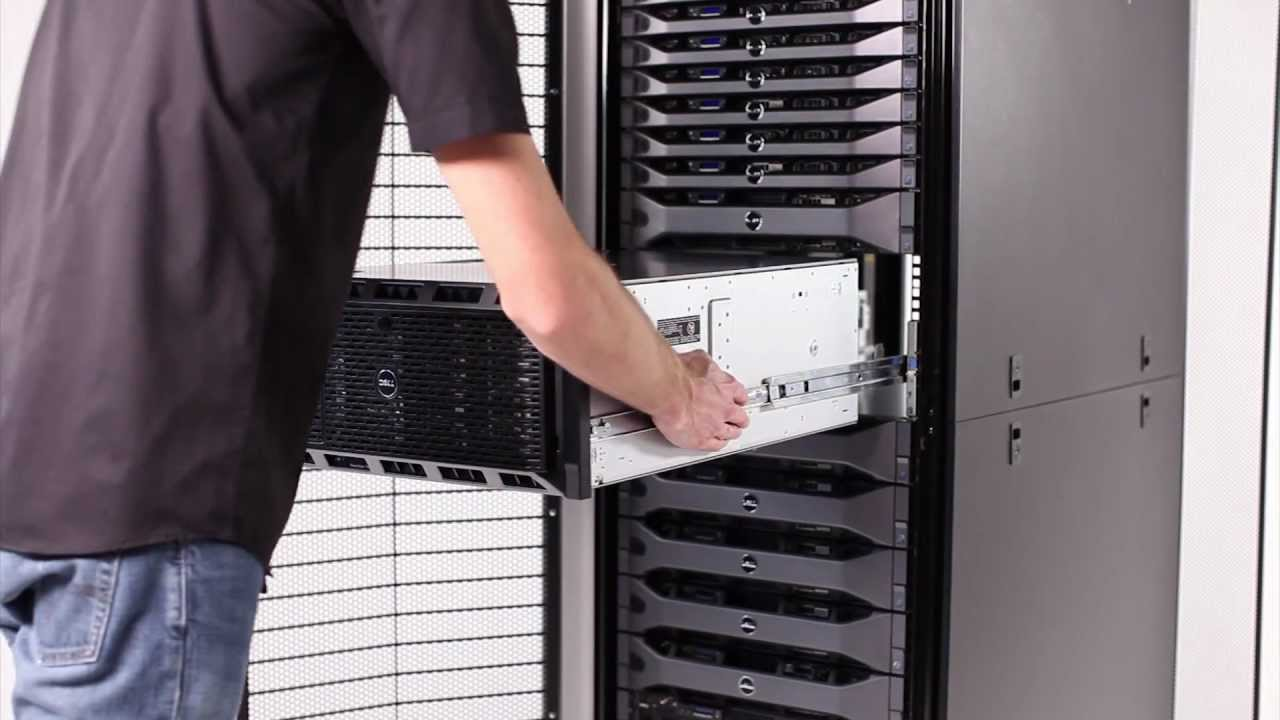

Rack and Stack performed by Remote Hands team
Escort:
As the data center has a strong access policy and any personnel not part of a pre-authorized access list will require an escort into designated areas in the data center by the Remote Hands team or site security officers. The escort is to ensure personnel do not loiter and move to non-permitted areas for security reasons. If you want to feel like a VIP, being escorted inside the data center will be a good experience.
PTW- Permit to Work:
Permit to Work is a formal written approval statement that is necessary for the Remote Hands team or vendors to have, before starting work within the facilities. This PTW provides a record and understanding by the data center operators on why and what kind of works are planned to be carried out in the data center. Without the necessary approved PTW, no personnel will be allowed to work.
MOS- Method Of Statement:
MOS is a detailed statement and procedure of the works that need to be carried out for successful completion of work therefore no surprises will be expected. The MOS list out how the works will be carried out in detail and providing the full explanation and method in which the works will be performed by the vendors or Remote Hands team.
Risk Assessment:
Risk assessment is a safety process of identifying hazards and risks associated with carrying out the work in the data center. This is a preventive measure to avoid any potential accidents.
Induction:
Before working in the data center, Remote hands technicians, and vendors will be inducted with training or certification conducted by the data center operator, which is typically a prerequisite if you wish to work in the data center. The induction process allows the person to understand the rules, environment conditions, security, and safety protocols before working in the facilities.
PUE:
PUE is power usage effectiveness. It’s an industry standard (ISO/IEC 30134-2:2016) that measures the ratio of energy used to the energy available. A perfect PUE would be 1. Most modern data centers have a PUE of about 1.2-1.4. Anything above 1.5 means you should be looking for energy improvements.
Raise Floor:
Raise floor is an elevated structural floor system above a concrete slab that is used to create a hidden void for the passage of services such as telecom, electrical & mechanical services but most importantly allows the cool airflow to cool down the racks.
The list can be a very long one but these are the most common terms among the Remote Hand’s engineer.
That marks an end to Part 5 of the Remote Hands Series. Stay tuned for Part 6 of the series. Remember to Follow us on social media.
If you are looking for what is Remote Hands and how it can benefit your organization, you can click to read Part 1 of the Remote Hand Series. Even better click here and we will connect with you and solve all your queries regarding Remote Hands personally.
Till then, Stay Safe.





